What Does Paradox Of Value Mean In Business Terms
Paradox of value is a puzzle raised by Adam Smith who was one of the great economists in 1700s. The Concept of Business Value Explained.
 The Stakeholder Paradox Stakeholder Theory
The Stakeholder Paradox Stakeholder Theory
March 8 2020 by Priya C.

What does paradox of value mean in business terms. The apparent contradiction between a high monetary value of a nonessential item and the low value of an essential item. Schwartz maintained that an overabundance of. Barry Schwartz wrote about the negative consequences of having too many options in his 2004 book The Paradox of Choice.
Most logical paradoxes are known to be invalid arguments but are still valuable in promoting critical thinking. They dont get resolved by tackling one demand at a time or by making a final decision. Paradoxes also described as polarities and sometimes mislabeled as problems are dilemmas that seem to defy common sense and business acumen.
Water is extremely useful and its TOTAL UTILITY is high but because it is generally so abundant its MARGINAL UTILITY and hence price is low. The paradox of choice is an observation that having many options to choose from rather than making people happy and ensuring they get what they want can cause them stress and problematize decision-making. The proposition that the value PRICE of a good is determined by its relative scarcity rather than by its usefulness.
The Paradox of Value is also known as the diamond-water paradox. For instance take the paradox of value. PMBOK defines business value as the entire value of the business.
The paradox of value also known as the diamondwater paradox is the contradiction that although water is on the whole more useful in terms of survival than diamonds diamonds command a higher price in the market. Whereas Value in Exchange is the price that an item fetches. The philosopher Adam Smith is often considered to be the classic presenter of this paradox although it had already appeared as early as Platos Euthydemus.
Beside this what does paradox of value mean. Monetary worth of a gs as determined by the market. Also known as the diamond-water paradox.
AQA Edexcel OCR IB Eduqas WJEC. This question is the diamond-water paradox also known as paradox of value and it was first presented by the economist Adam Smith in the 1700s. Examples of tangible elements include monetary assets stockholder equity fixtures and utility.
This type of paradox arises when expectations and common sense are evidently at odds with reality. Paradox of Value. Diamond-Water Paradox is defined as the difference between the value in use and the exchange value of any product.
The business value is the standard value measure used in business valuation. The factor which majorly influences the Paradox of Value is the Value in Exchange. A little less commonly a paradox can also be a conclusion that intuitively seems illogical yet which could potentially be demonstrated as true.
A paradox is an argument that produces an inconsistency typically within logic or common sense. Smith questioned the enigma of a diamond being less useful than water still it has a higher exchange value. The total sum of all tangible and intangible elements.
What is the definition of value. However some have revealed errors in definitions assumed to be rigorous and have caused axioms of mathematics and logic to be re-examined. But water typically has a low market price while diamond jewellery has a high market price.
Usually an item with lower utility tends to have a higher value in exchange and lower value in use and hence bears a higher price which now explains why the price of diamond was higher than water. How to Manage Paradox. The paradox of value also known as the diamondwater paradox is the apparent contradiction that although water is on the whole more useful in terms of survival than diamonds diamonds command.
But advocates of looking at business as paradox say that its requirement for balanced consideration of alternatives has a value that many hot trends in management dont. What is the definition of paradox of value. We understand that water is necessary to our life and that ornaments such as diamonds are not life-sustaining.
Conflicting demands and eitheror tensions are the norm for many managers. Why More is Less. In the context of business leadership a paradox refers to a pair of characteristics that appear to be so different that they really couldnt exist together.
Diamonds by contrast are much less useful than water but their great scarcity makes their marginal utility and. The paradox of value also known as the diamondwater paradox is the contradiction that although water is on the whole more useful in terms of survival than diamonds diamonds command a higher price in the market.
 The Paradox That Is Colombia Business Blog Colombia Paradox
The Paradox That Is Colombia Business Blog Colombia Paradox
 The Digital Ecosystem Paradox Learning To Move To Better Digital Design Outcomes Digital Innovation Technology Paradox
The Digital Ecosystem Paradox Learning To Move To Better Digital Design Outcomes Digital Innovation Technology Paradox
 Why You Should Rethink The Merchant Cash Advance Small Business Loans Small Business Funding Personal Finance
Why You Should Rethink The Merchant Cash Advance Small Business Loans Small Business Funding Personal Finance
 Organizational Dynamism And Adaptive Business Model Innovation The Triple Paradox Configuration Sciencedirect
Organizational Dynamism And Adaptive Business Model Innovation The Triple Paradox Configuration Sciencedirect
 Examples Of Selected 10 Strategic Paradoxes In Yin And Yang Concept Download Table
Examples Of Selected 10 Strategic Paradoxes In Yin And Yang Concept Download Table
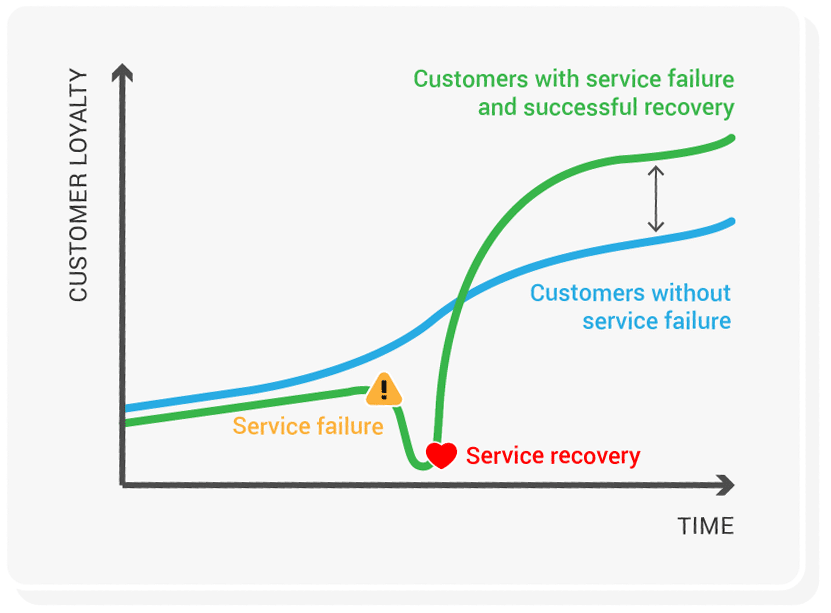 The Service Recovery Paradox Customer Thermometer
The Service Recovery Paradox Customer Thermometer
 What Is Utility Function Definition And Explanation Choice Theory Basic Concepts Definitions
What Is Utility Function Definition And Explanation Choice Theory Basic Concepts Definitions
 Image Result For Paradox Examples My Family Essay Essay You Are The Father
Image Result For Paradox Examples My Family Essay Essay You Are The Father
 Paradox Google Search Paradox Funny Quotes Life
Paradox Google Search Paradox Funny Quotes Life
 What Is The Discounted Dividend Model Theory Formula Tips Toolshero Dividend Model Theory Financial Management
What Is The Discounted Dividend Model Theory Formula Tips Toolshero Dividend Model Theory Financial Management
 The Service Recovery Paradox Customer Thermometer
The Service Recovery Paradox Customer Thermometer
 Time Value Of Money Time Value Of Money Business Powerpoint Templates How To Create Infographics
Time Value Of Money Time Value Of Money Business Powerpoint Templates How To Create Infographics
 058 Defining Your Core Values Productivity Paradox Core Values Mind Reading Tricks Cognitive Therapy
058 Defining Your Core Values Productivity Paradox Core Values Mind Reading Tricks Cognitive Therapy
 Sn10 12 Sketchnotes The Paradox Of Choice Ted Talk From Barry Schwartz Lettering Paradox Psychology
Sn10 12 Sketchnotes The Paradox Of Choice Ted Talk From Barry Schwartz Lettering Paradox Psychology
 How To Manage Paradox Center For Creative Leadership
How To Manage Paradox Center For Creative Leadership
 The Paradox Of How Groups Of People Are Able To Take Actions That No One In The Group Actually Thinks Is A Good I Paradox Critical Thinking New Things To Learn
The Paradox Of How Groups Of People Are Able To Take Actions That No One In The Group Actually Thinks Is A Good I Paradox Critical Thinking New Things To Learn
 Understanding Demand And Supply Paradoxes And Their Role In Business To Business Firms Sciencedirect
Understanding Demand And Supply Paradoxes And Their Role In Business To Business Firms Sciencedirect
 Understanding Demand And Supply Paradoxes And Their Role In Business To Business Firms Sciencedirect
Understanding Demand And Supply Paradoxes And Their Role In Business To Business Firms Sciencedirect
 The Mother Of All Innovation Challenges Innovation Challenge Process Chart Innovation
The Mother Of All Innovation Challenges Innovation Challenge Process Chart Innovation